Basic fundamental concepts on virtualization from VMware vSphere Client help guide.
What is Virtualization ?
- Virtualization is an abstraction layer that breaks hard connection between physical hardware and operating system.
- A virtual infrastructure is an enterprise-wide solution that provides fluid,powerful computing that maximize resource utilization and cost savings.
- Virtual machines are the key element to a virtual infrastructure.
- Virtualization allows you to run multiple virtual machines with different operating systems and applications to run in isolation,side by side on the same physical machine.
- Using virtualization , you can dynamically move resources where they are needed and processing where it makes more sense.
What is Virtual Machine ?
- A virtual machine is a software computer that like a physical computer, runs an operating system and applications.
- An operating system installed on a virtual machine is called a guest operating system.
- Every virtual machine has virtual devices that provide the same functionality as physical hardware. Virtual machine gets CPU & memory,video cards,access to storage, and network connectivity from the hosts they run on.
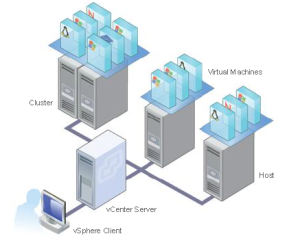
- Virtual machines run on hosts and clusters. Multiple virtual machines can run on the same host and cluster at the same time.
- Virtual machines are not emulators or simulators. They are real machines that can do the same things physical computers can do and more. Because of the flexibility of virtual machines, physical computers become less a way to provide service (applications, database and so on) and more a way to house the virtual machines that provide those services.
Benefits of virtual machines
- Physical machines are hard to move,difficult to copy and bound to a specific set of hardware. Virtual machines are easy to copy and move because they are independent of physical hardware.
- Virtual machines are easy to manage because they are isolated from other virtual machines running on same physical hardware and insulated from physical-hardware changes.
- Freedom from physical hardware constraints : virtual machines allow the operations of different operating system running across different hardware.
- Backup and Recovery with little or no down-time : You can configure virtual machines with operating systems and applications once and then clone them many times. Backing up a virtual machine is as easy as backing up few files. In this way virtual machine ensures fast deployment and reliability.
- Greater resource utilization : Multiple virtual machines can run on the same physical server. In addition consolidating computing power to fewer physical computers can substantially increase power savings in your enterprise.
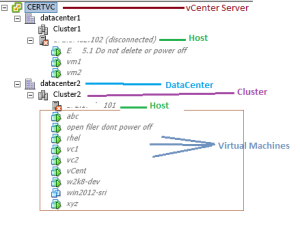
What is Host ?
- A host is a computer that uses virtualization software such as ESX or ESXi to run virtual machines.
- Host provides CPU & memory resources that virtual machines use, and give virtual machines access to storage and network connectivity.
- You can add virtual machine to a host by creating a new one or deploying a virtual appliance.
- A virtual appliance is a pre-built virtual machine with an operating system and software already installed.
What is Datacenter ?
- A datacenter is a primary container of inventory objects such as hosts and virtual machines.
- From the datacenter, you can add and organize inventory objects. Typically, you add hosts,folders, and clusters to a datacenter.
- The vCenter Server can contain multiple datacenters. Large companies might use multiple datacenters to represent organizational units in their enterprise.
- Inventory objects can interact within datacenters,but interaction across datacenters are limited.For example, you can move virtual machine across hosts within a datacenter but not to host in another datacenter.
What is Cluster ?
- A cluster is a group of hosts that share resources and a management interface.
- When you add a host to a cluster,the host’s resources become part of the cluster’s resources.
- The cluster manages the resources of all hosts within it.
- Cluster enable the vSphere Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) and vSphere High Availability (HA) solutions. vSphere DRS continuously balances virtual machine workloads across your ESX/ESXi hosts. vSphere HA allows the virtual machines running on ESX/ESXi hosts to automatically recover from host failures.
What is Resource Pool ?
- A resource pool provides a way to divide the resources of a stand-alone host or a cluster into smaller pools.
- A resource pool is configured with a set of CPU and memory resources that the virtual machines that run in resource pool share.
- Resource pools are self contained and isolated from other resource pools.
- You can combine multiple physical servers into a single resource pool that aggregates CPU and memory capacity.
- Virtual machines execute in and draw their resources from resource pools.
- This arrangement allows virtual machine workloads to continuously balance across resource pools. When the workload increases, the vCenter Server automatically allocates additional resources and transparently migrates virtual machines between hosts in the resource pool.
Using vSphere
- vSphere is a software solution for deploying and managing virtual machines across a datacenter.
- VMware vSphere is a system for managing virtual infrastructure.
- VMware vCenter server is a tool that manages multiple host servers that run multiple virtual machines.
- With vSphere, datacenters can instantly provision servers, globally manage resources and eliminate scheduled downtime for hardware maintenance.
What is vCenter Server ?
- VMware vCenter Server provides a convenient single point of control to the datacenter.
- It runs on top of windows server to centrally manage your vmware ESX/ESXi hosts and provides essential datacenter services such as access control,performance monitoring and configuration.
- vCenter server brings resources together from individual hosts to be shared among virtual machines in the entire datacenter.
- It accomplishes this by managing the assignment of virtual machines to the hosts and the assignment of resources to the virtual machines within a given host based on the policies that the system administrator sets.
- vCenter Server allows the use of advanced vSphere features such as vSphere DRS, vSphere HA, and vMotion.
- With vCenter Server, we can quickly provision new server virtual machines and create a library of standardized virtual machine templates so your newly provisioned systems always conform to your datacenter requirements.
- vCenter Server lets us migrate running virtual machines between host servers so that you can perform hardware maintainance with minimal downtime.
- vCenter Server allows us to balance virtual machine workloads across hosts and manage virtual machines for high availability and disaster recovery.
What is vSphere Client ?
- The vSphere Client is a primary interface for creating, managing and monitoring virtual machines,their resources and their hosts.
- It also provides console access to virtual machines.
- The vSphere Client is installed on a windows machine with network access to your vCenter Server or your ESX/ESXi host.
- The interface displays different options depending on which type of server you are connected to.
- Although vCenter Server performs all vSphere activities,you use the vSphere Client to monitor,manage and control vSphere server.
- A single vCenter Server or ESX/ESXi host can support multiple,simulteneously connected vSphere Clients.
What is virtual hardware?
- Just as a physical computer has hardware devices such as CPU and memory, a virtual machine has virtual hardware devices.
- If we look at a virtual machine’s configuration, we find virtual CPU, memory, hard disks, CD/DVD drives, floppy drives,Ethernet adapters, sound cards, and so on.
- Each virtual device performs the same function for the virtual machine as does the hardware on a physical computer.
- Virtual hardware lets the virtual machine divide up the physical hardware as needed. For example, we can run many virtual machines on a single physical CPU, each appearing to have its own virtual CPU.
- We can move a virtual machine from one host to another and the mappings between the virtual and physical devices change automatically, while the virtual devices remain unchanged.
- Virtual hardware, virtual machines are insulated from the details of physical hardware.
Inventory views in vSphere Client
- Inventory view provides views of all objects that the vCenter Server manages, such as datacenters, resource pools, clusters, networks, datastores, datastore clusters, templates, hosts and virtual machines.
- The four inventory views are :
- Hosts and Clusters : Displays the inventory hierarchy of all inventory objects except templates, networks, and datastores.
- Virtual machines & Templates : Displays the list of virtual machines and templates.
- Networks : Displays the list of networks.
- Datastores & Datastore Clusters : Displays the list of datastores and datastore clusters.
Storage in vSphere
- Every virtual machine uses a virtual hard disk to store its operating system, program files, and other data associated with its activities.
- A virtual disk is a large physical file, or a set of files, that can be copied, moved, archived, and backed up as easily as any other file.
- Virtual disk files are stored on dedicated storage space on a variety of physical storage systems, including internal and external devices of a host, or networked storage, dedicated to the specific tasks of storing and protecting data.
- A host can discover storage devices to which it has access and format them as datastores.
- The datastore is a special logical container, analogous to a file system on a logical volume, where hosts place virtual disk files and other files that encapsulate essential components of a virtual machine.
- Datastores can hide specifics of different storage products and provide a uniform model for storing virtual machine files.
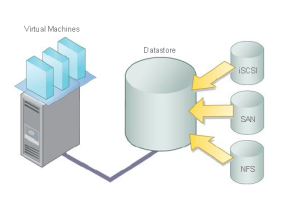
What is Datastore ?
- A datastore is a logical container that holds virtual machine files and other files necessary for virtual machine operations.
- Datastores can exist on different types of physical storage, including local storage, iSCSI (internet Small Computer System Interface), Fibre Channel SAN (Storage Area Network), or NFS.
- A datastore can be VMFS-based (Virtual Machine File System) or NFS-based (Network File System).
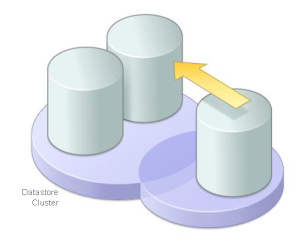
What is Datastore Cluster ?
- A datastore cluster is a collection of datastores that share resources and a management interface.
- When you add a datastore to a datastore cluster, the cluster’s resources become part of the datastore cluster’s resources.
- You use datastore clusters to aggregate storage resources, which enables you to support resource allocation policies at the datastore cluster level.
- When you create a datastore cluster, you can use Storage DRS to manage storage resources. The I/O load balancing functionality available with Storage DRS is available only when all hosts connected to the datastores in the datastore cluster.
What is Networks view ?
- This view displays the set of networking objects available on vCenter.
- Using the Networking view, you can create and manage networking with vSphere Distirbuted Switches and networking with Standard Switches configuration.
- vSphere Distributed Switches manages virtual machines and host networking at datacenter level.
- vSphere Standard Switches manages virtual machines and host networking at host level.
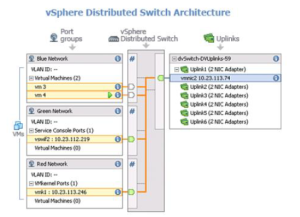
Setting up vSphere Distributed Switch Architeracture (In vSphere Client)
- The first step in setting up a networking environment using vSphere Distributed Switches is to create a vSphere Distributed Switch in the Networking inventory view of the vSphere Client.
- vSphere Distributed Switches are created at the datacenter level in the Networks view of the vSphere Client.
- After a vSphere Distributed Switch is created, hosts and distributed port groups can be added to it.
- Host networking options are configured through the individual host networking configuration page or using host profiles.
- Finally, virtual machine NICs are connected to the distributed port groups. Connect virtual machine NICs through individual virtual machine NIC configuration or by migrating virtual machine networking from the vSphere Distributed Switch itself.
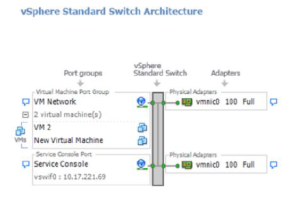
Setting up vSphere Standard Switch architecture
- Switches can be done from the Configuration tab of the host view.
- Port groups for virtual machine networking or networking services, such as service console networking, vMotion, and iSCSI networking, are configured using the Add Networking Wizard.
- New Standard Switches can be created during the port group creation process, or you can connect your new port group to an already existing Standard Switch.
- A virtual machine is connected to a virtual network by assigning the virtual machine’s NIC to that network’s port group.